Use Cases¶
With the pykCSD toolbox you can estimate 1D, 2D and 3D potentials and CSD based on your input data. Here are the basic examples for each of the reconstructions.
Sample 1D reconstruction¶
You can estimate potentials measured with electrodes placed along a line:
from pykCSD.pykCSD import KCSD
import numpy as np
#the most inner list corresponds to a position of one electrode
elec_pos = np.array([[-0.5], [0], [1], [1.5], [3.5], [4.1], [5.0], [7.0], [8.0]])
#the most inner list corresponds to a time recording made with one electrode
pots = np.array([[-0.1], [0.3], [-0.4], [0.2], [0.8], [0.5], [0.2], [0.5], [0.6]])
#you can define model parameters as a dictionary
params = {
'xmin': -3.0,
'xmax': 12.0,
'source_type': 'gauss',
'n_sources': 30
}
k = KCSD(elec_pos, pots, params)
k.estimate_pots()
k.estimate_csd()
k.plot_all()
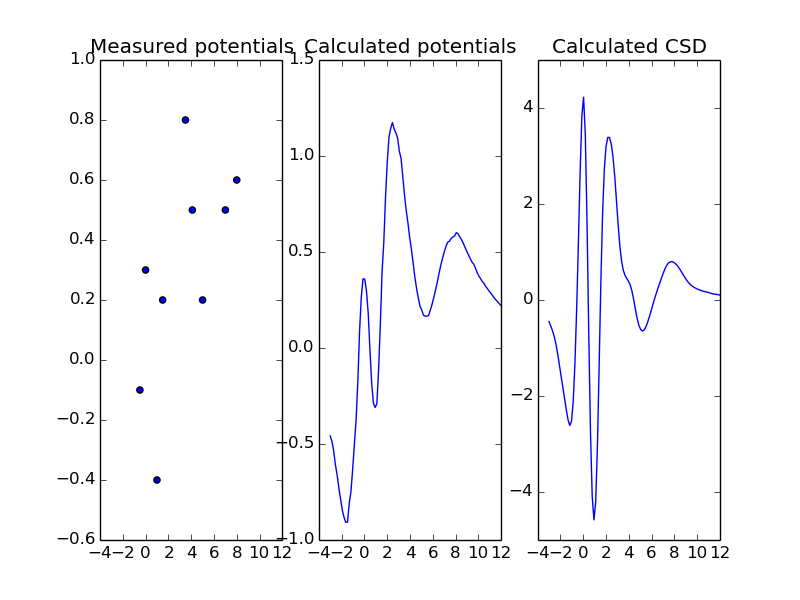
The sample reconstruction in 1D
Cross validation¶
Having your kCSD solver set up, you can use cross validation to regularize your results:
from pykCSD import cross_validation as cv
from sklearn.cross_validation import LeaveOneOut
index_generator = LeaveOneOut(len(elec_pos), indices=True)
lambdas = np.array([10000./x**2 for x in xrange(1, 50)])
k.solver.lambd = cv.choose_lambda(lambdas, pots, k.solver.k_pot, elec_pos, index_generator)
print k.solver.lambd
k.estimate_pots()
k.estimate_csd()
k.plot_all()
>> 4.16493127863
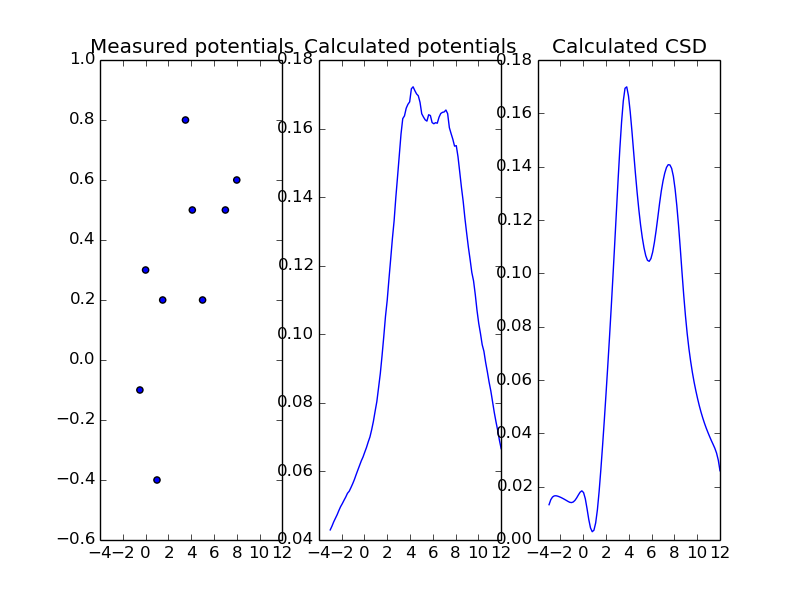
The same reconstruction regularized with cross validation
Sample 2D reconstruction¶
You can estimate potentials and CSD measured with planar electrodes:
from pykCSD.pykCSD import KCSD
import numpy as np
elec_pos = np.array([[-0.2, -0.2],[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1,1], [0.5, 0.5], [1.2, 1.2]])
pots = np.array([[-1], [-1], [-1], [0], [0], [1], [-1.5]])
params = {'gdX': 0.05, 'gdY': 0.05, 'xmin': -2.0, 'xmax': 2.0, 'ymin': -2.0, 'ymax': 2.0}
k = KCSD(elec_pos, pots, params)
k.estimate_pots()
k.estimate_csd()
k.plot_all()
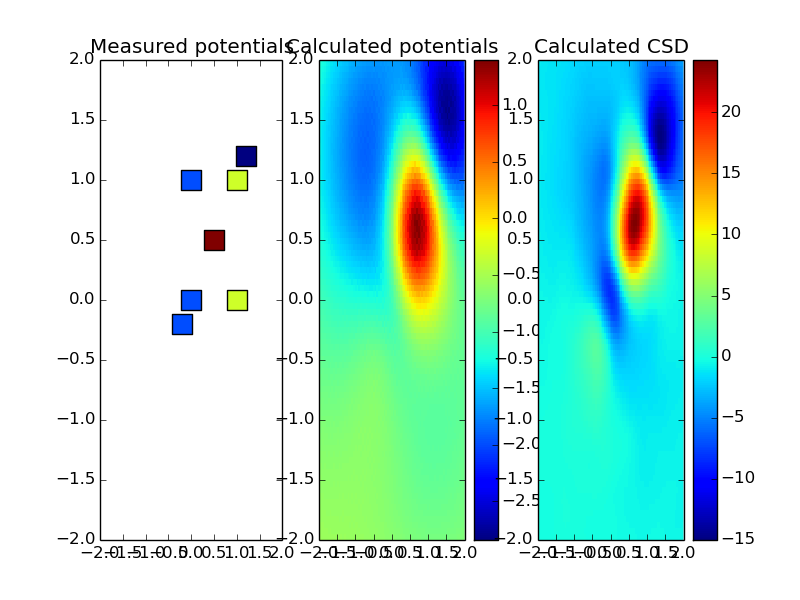
The sample reconstruction in 2D
Sample 3D reconstruction¶
You can also recostruct CSD and LFP using measurements taken by spatial electrodes:
from pykCSD.pykCSD import KCSD
import numpy as np
elec_pos = np.array([(0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0), (1, 0, 0),
(0, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 1),
(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)])
pots = np.array([[-0.5], [0], [-0.5], [0], [0], [0.2], [0], [0], [1]])
params = {
'gdX': 0.05,
'gdY': 0.05,
'gdZ': 0.05,
'n_sources': 64,
}
k = KCSD(elec_pos, pots, params)
k.estimate_pots()
k.estimate_csd()
k.plot_all()
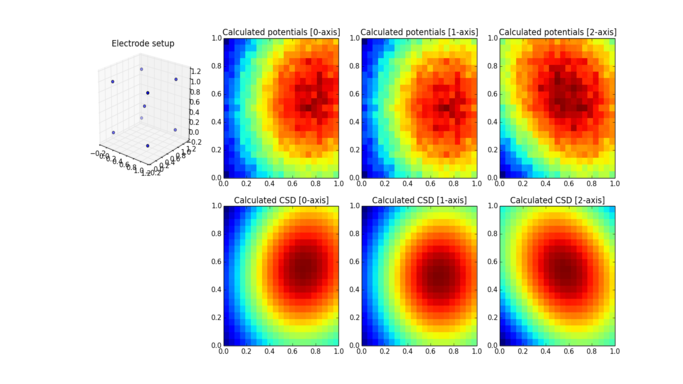
The sample reconstruction in 3D
Such a dataset can be also visualized using mayavi:
from mayavi import mlab
csd = k.solver.estimated_csd[:,:,:,0]
#setting up a proper gui backend
%gui wx
mlab.pipeline.image_plane_widget(mlab.pipeline.scalar_field(csd),
plane_orientation='x_axes',
slice_index=10,
)
mlab.pipeline.image_plane_widget(mlab.pipeline.scalar_field(csd),
plane_orientation='y_axes',
slice_index=10,
)
mlab.outline()
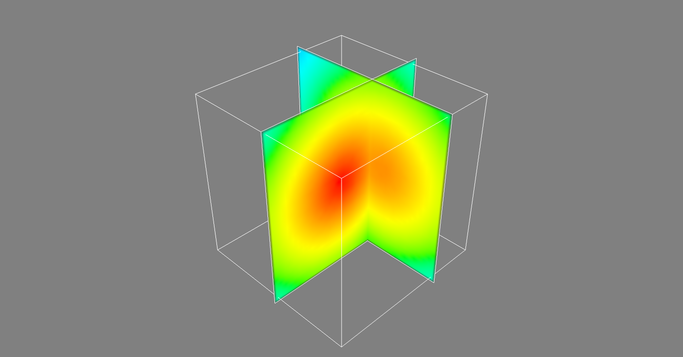
The same reconstruction visualized with mayavi